Numbers are the basic units of mathematics same as a cell is a basic unit of a life. There are several types of numbers exists, and all of them are categorized into two main categories : Real numbers and Imaginary numbers (or Complex numbers).
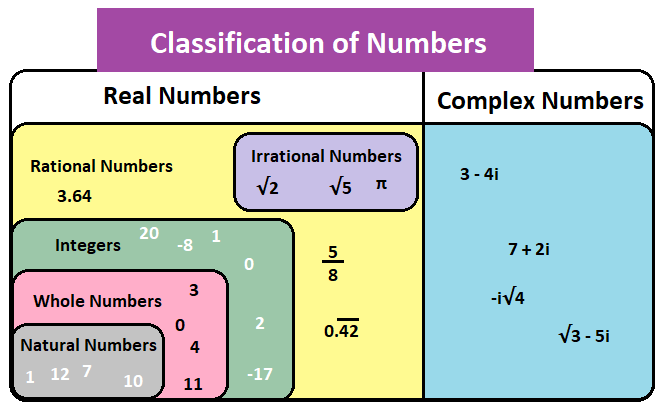
The term “real numbers” originated as a way to distinguish them from “imaginary numbers.”. Mathematicians in the early days first worked with natural numbers (1, 2, 3, …) and later expanded to include integers (negative numbers) and rational numbers (fractions). Eventually, they discovered numbers that couldn’t be expressed as fractions, like irrational numbers (e.g., π, √2 ). Together, these numbers formed what we now call the real number system. Basically, they are all the numbers that can be represented on the number line.
During the 16th and 17th centuries, mathematicians encountered equations like:
x² + 1 = 0
x² = -1
which has no real solution because the square root of -1 is not a real number. To solve such equations, they introduced a new type of number called imaginary numbers, where ii (the imaginary unit) is defined as: i=√ -1
To differentiate between these newly introduced imaginary numbers and the numbers already in use, the older number system was named “real numbers.” The name doesn’t mean they are more “real” than imaginary numbers—it’s just a historical distinction.
- Real Numbers: This set includes all rational and irrational numbers, essentially covering all the numbers on the number line.
- Complex Numbers: Numbers that have a real part and an imaginary part (e.g., 3 + 4i, where i is the imaginary unit).
- Natural Numbers: These are the set of positive integers starting from 1, 2, 3, and so on. They are used for counting.
- Whole Numbers: This set includes all natural numbers plus zero (0, 1, 2, 3, …).
- Integers: These consist of positive and negative whole numbers, including zero (…, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …).
- Rational Numbers: Any number that can be expressed as a fraction or ratio of two integers (e.g., 1/2, -3/4, 5).
- Irrational Numbers: These cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Their decimal representations are non-repeating and non-terminating (e.g., π, √2).
Math is like a puzzle, and you learn every day something new!
Unlock your potential with personalized tutoring at Sharma & Sharma Tutoring Services, from elementary school to adulthood. We’re your math superheroes!. We also provide services in other subjects. Contact us to learn more. You can also turn in to our blog for more insights. Gift cards are also available for tutoring sessions.
Cheers!! ❤
Sharma & Sharma Tutoring Services
Private Tutoring & Exam Prep Services
www.mathtutorofflorida.com
