IRRATIONAL NUMBER has been the most misunderstood, and often the scariest number classification of the number system for students. The reason is simple, they don’t understand it correctly. Though irrational numbers have been very useful in many precision related measurements and hence, they are our friends :) .Let’s take a deep dive and understand it better..
There are various type of numbers that we use daily. All the numbers are primarily part of a basic category called as Complex numbers. You can say, this is a super set (or Universal set of numbers). Complex Numbers can be expressed as a sum of a real part and an imaginary part.
Complex numbers are of the form: a + bi

where ‘a’ and ‘b’ are real numbers and ‘i’ is the imaginary unit.
Real Numbers are the set of all possible numbers on the number line. They are denoted as R. The real numbers are further subdivided into Rational and Irrational numbers.
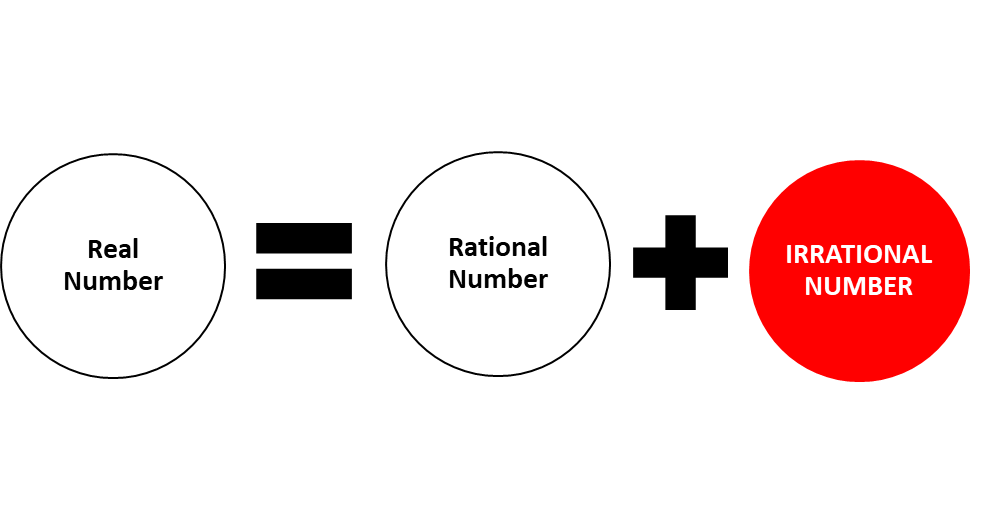
Rational Numbers are those numbers that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers, with a non-zero denominator. meaning they are written in the form of P/Q , such as 3/4, 5/6, -2/3, or 8 etc. This category includes integers and fractions, denoted as Q.
IRRATIONAL NUMBERS are those numbers that cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. It means you cannot expresses them in the P/Q form. Irrational numbers are fascinating as they cannot be expressed as fractions and their decimal expansions are non-repeating and non-terminating, such as √2, π, and e.
What are the various classification of Irrational numbers?
Square Root Irrationals
These are numbers that arise as the square root of a non-perfect square. Examples include √2, √3, √5, √7, and so on. These numbers cannot be expressed as fractions or terminating decimals.
Cube Root Irrationals
These are numbers that arise as the cube root of a non-perfect cube. Examples include ∛2, ∛3, ∛5, ∛7, and so on. Like square root irrationals, these numbers cannot be expressed as fractions or terminating decimals.
Transcendental Numbers
These irrational numbers are not algebraic, meaning they are not a root of any polynomial equation with integer coefficients. Examples include π (pi) and e (Euler’s number). These numbers have non-repeating and non-terminating decimal representations.
Non-repeating & Non-terminating Decimals
There are irrational numbers that cannot be expressed as fractions and have decimal representations that neither terminate nor repeat. Examples include numbers like 0.101001000100001…, 0.12345678910111213…, and so on.
Algebraic Irrationals
These irrational numbers are roots of polynomial equations; however, they are not rational numbers. Examples include √2, which is a root of the equation x^2 – 2 = 0, and √3, which is a root of the equation x^2 – 3 = 0.
Why Irrational numbers are important?
Irrational numbers hold significant importance in mathematics and its applications.
Completeness of the Real Number System: By including irrational numbers, the real number system becomes complete, allowing us to represent any quantity on the number line without any gaps.
Exact Representations of Some Quantities: Irrational numbers provide exact representations for quantities that cannot be expressed as fractions or decimals. For example, √2 represents the ratio of the diagonal to the side of a square. Without irrational numbers, we would be limited to approximations, which may not be sufficiently precise for certain applications.
Foundation of Geometry: Irrational numbers play a crucial role in geometry, where they represent lengths and measurements of line segments, diagonals, or curves. They help describe the relationships between geometric figures and allow for more accurate calculations.

Essential in Calculations and Formulas: Many mathematical formulas, equations, and calculations involve irrational numbers. For instance, trigonometric functions, exponential functions, and logarithmic functions frequently produce irrational outputs, making irrational numbers indispensable in applied mathematics, engineering, and physics.
Encryption and Security: The properties of irrational numbers, such as being non-repeating and non-terminating, are utilized in cryptographic algorithms to enhance security. The inclusion of irrational numbers in encryption methods makes them more resistant to decryption techniques.
Aesthetic and Creative Pursuits: Irrational numbers contribute to the realm of aesthetics and creativity. They are found in music, art, and architecture, where they are employed to create patterns, rhythms, and harmonies that are pleasing to the human senses.
In summary, irrational numbers are essential for representing precise quantities, providing solutions to equations, advancing various fields of science and engineering, and enriching our understanding of the world around us.
Cheers! ❤️
Subscribe To Our Blogs :

Happy Holloween😂
Sent from my iPhone
Happy Halloween, Sir! :)